Step into the fascinating world of Tudor houses, a captivating architectural style that reflects a pivotal period in English history. From grand manor houses to cozy timber-framed cottages, these structures tell a story of changing tastes, evolving building techniques, and the lives of those who inhabited them. Let’s delve into the defining characteristics and enduring appeal of Tudor architecture.
Defining Characteristics of Tudor Houses
Tudor houses, built primarily between the 15th and 17th centuries, are easily recognizable by their distinct features. Common elements include steeply pitched roofs, often with multiple gables, prominent chimneys, and decorative half-timbering.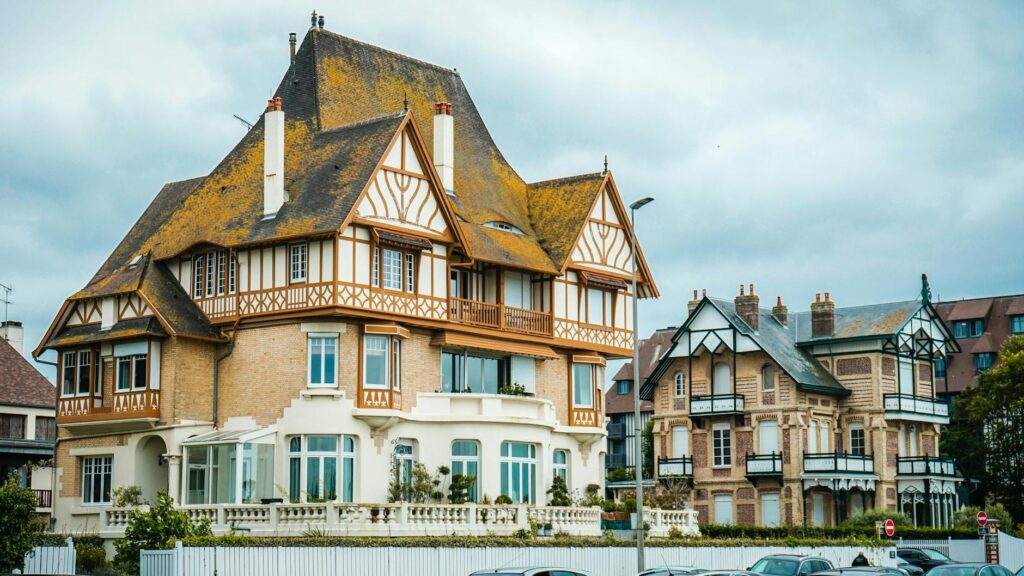  The use of exposed timber framing, filled with wattle and daub or brick, was a hallmark of the era, creating a visually striking and durable structure. Many examples also boast oriel windows, projecting bay windows that add both charm and functionality.
The use of exposed timber framing, filled with wattle and daub or brick, was a hallmark of the era, creating a visually striking and durable structure. Many examples also boast oriel windows, projecting bay windows that add both charm and functionality.
The Rise of Brick and Stone
While timber framing was prevalent, Tudor architecture saw a significant increase in the use of brick and stone, particularly in larger houses. This reflects the growing availability of these materials and a shift towards more substantial construction. [IMAGE_2_HERE] The combination of brick and timber often created a visually rich and textured façade. The use of these materials also contributed to the longevity and strength of these structures, many of which still stand today.
Interior Features and Design
Inside Tudor houses, one might find grand fireplaces as central focal points, reflecting the importance of warmth and hearth in the colder English climate. The interiors often featured intricate wood paneling, showcasing craftsmanship and attention to detail. Larger homes might include multiple stories and elaborate staircases. [IMAGE_3_HERE] The layout and size of the interior varied greatly depending on the wealth and status of the inhabitants.
Notable Examples of Tudor Architecture
Across England, many stunning examples of Tudor houses remain, offering a glimpse into the past. From grand manor houses like Hampton Court Palace to smaller, more modest dwellings, these buildings showcase the diversity and adaptability of the style. A visit to these historic sites is highly recommended for anyone interested in architectural history. You can explore some of the most famous examples by visiting this website dedicated to Tudor architecture.
The Social Context of Tudor Homes
Tudor houses were not just buildings; they were a reflection of the social and economic conditions of the time. The size, design, and materials used often indicated the wealth and status of the occupants. Larger, more ornate houses belonged to the aristocracy and gentry, while smaller, simpler houses were typical of the peasantry and merchant classes. Understanding this social context adds another layer of richness to the appreciation of Tudor architecture.
The Enduring Legacy of Tudor Style
The Tudor architectural style has left an indelible mark on English heritage and continues to inspire architects and designers today. Its distinctive features and timeless appeal make it a popular choice for new constructions and renovations. The unique blend of timber, brick, and stone, alongside the steeply pitched roofs and decorative elements, creates a look that is both elegant and rustic. Many modern homes incorporate Tudor-inspired elements, paying homage to this iconic style. Learn more about the evolution of Tudor architecture by reading this in-depth article.
Evolution and Variations
While there are common characteristics, Tudor architecture isn’t monolithic. The style evolved over time, influenced by changing fashions, building materials, and regional variations. Early Tudor styles differ significantly from later Jacobean styles, which followed. These variations reflect the dynamic nature of the period and the creativity of the builders. For further reading on the diversity within Tudor style, check out this academic resource.
Construction Techniques and Materials
The construction methods employed in Tudor houses reflect the available technology and materials of the time. Timber framing, wattle and daub, brickwork, and stone were skillfully combined to create durable and aesthetically pleasing structures. Understanding these techniques allows for a deeper appreciation of the craftsmanship involved in building these iconic homes. [IMAGE_4_HERE]
In conclusion, Tudor houses stand as a testament to a significant era in English history, showcasing a unique blend of architectural features and social contexts. Their enduring appeal continues to captivate and inspire, making them a truly remarkable subject of study and admiration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key features of a Tudor house? Steeply pitched roofs, prominent chimneys, decorative half-timbering, and oriel windows are all key features.
What materials were typically used to build Tudor houses? Timber framing, wattle and daub, brick, and stone were all commonly used materials.
What is the difference between Tudor and Elizabethan architecture? While both styles share some similarities, Elizabethan architecture (following Tudor) generally features more elaborate ornamentation and symmetrical designs.
Where can I see examples of Tudor houses? Many well-preserved examples of Tudor houses can be found throughout England, including Hampton Court Palace.
How are modern homes influenced by Tudor architecture? Modern homes often incorporate Tudor-inspired elements such as steeply pitched roofs, gables, and decorative half-timbering.