Shallow foundations are a common type of foundation used for buildings that have a relatively low weight and are built on stable soil conditions. They are typically constructed by pouring concrete directly onto the ground or excavating a shallow trench and then pouring concrete.
Shallow Foundations
A shallow foundation is a type of building foundation that transfers structural load to the Earth very near to the surface, rather than to a subsurface layer or a range of depths, as does a deep foundation.
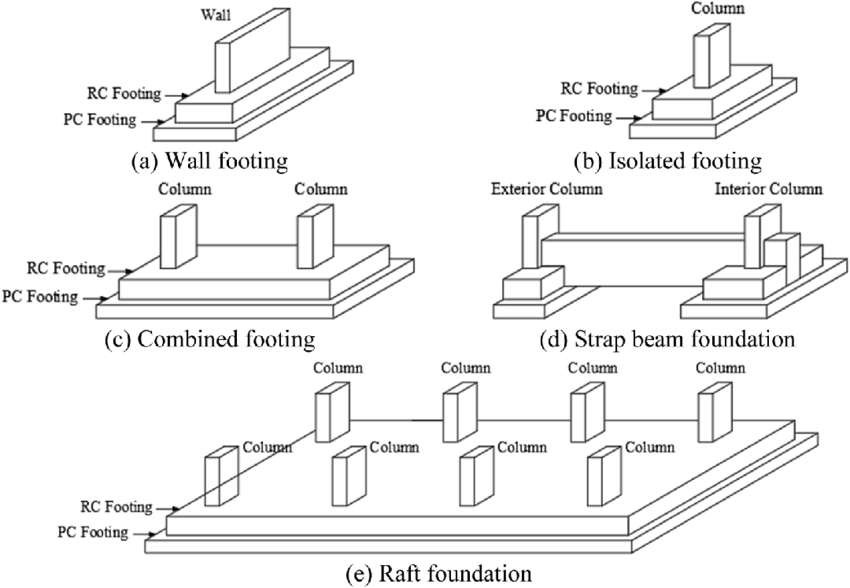
Types of Shallow Foundations:
- Slab-on-Grade: This is the simplest type of shallow foundation. It consists of a concrete slab poured directly onto the ground, often with a layer of insulation beneath it. Slab-on-grade foundations are commonly used for smaller residential and commercial buildings.
- Combined Footing: Combined footings are used to support multiple columns or walls. They are often used in areas where the soil is uneven or soft.
- Wall Footing: Wall footings are used to support the foundation walls of a building. They are typically wider than the walls themselves to provide additional support.
Advantages of Shallow Foundations:
- Simple and cost-effective: Shallow foundations are generally less expensive and easier to construct than deep foundations.
- Suitable for stable soil conditions: They are well-suited for areas with stable soil that can support the weight of the building.
- Quick construction: Shallow foundations can be constructed relatively quickly, reducing construction time.
Disadvantages of Shallow Foundations:
- Limited load capacity: Shallow foundations may not be suitable for heavy loads or buildings with multiple stories.
- Susceptible to frost heave: In areas with cold climates, shallow foundations may be susceptible to frost heave, which can cause the foundation to shift or crack.
- Not suitable for unstable soil: Shallow foundations are not suitable for areas with soft or unstable soil.
When to Choose Shallow Foundations:
Shallow foundations are a good choice for smaller buildings that are located on stable soil conditions. However, it’s important to consult with a structural engineer to determine the most appropriate foundation type for your specific project.